Java Basics:While loop examples scenarios in Selenium
While Loop
Let us now look into while loop fir selenium and where we use while loop in selenium. There are many places where this 'while' loop is used when writing selenium tests like
1) Reading data from properties file
2) Reading data from excel files
3) Retrieving values from database
The below is the sample code to read the data from properties file until it has completed reading the values from properties file, which is validated using 'KeyValues.hasMoreElements()'.
Check out for full example here read the data from properties file using while
while (KeyValues.hasMoreElements()) {
String key = (String) KeyValues.nextElement();
String value = prop.getProperty(key);
System.out.println(key + ":- " + value);
}
Read data from Properties file using Java Selenium
In Selenium .properties files are mainly used to store GUI locators / elements, and also Global fields like database configuration details
'.properties' files are mainly used in Java programs to maintain project configuration data, database config or project settings etc. Each parameter in properties file are stored as a pair of strings, in key and value format, where each key is on one line. You can easily read properties from some file using object of type Properties.
Below is a example program which demonstrate to read the data from .properties file using Java.
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Properties;
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.firefox.FirefoxDriver;
public class ReadFileData {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("D:/Dev/ReadData/src/datafile.properties");
FileInputStream fileInput = null;
try {
fileInput = new FileInputStream(file);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Properties prop = new Properties();
//load properties file
try {
prop.load(fileInput);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
WebDriver driver = new FirefoxDriver();
driver.get(prop.getProperty("URL"));
driver.findElement(By.id("Email")).sendKeys(prop.getProperty("username"));
driver.findElement(By.id("Passwd")).sendKeys(prop.getProperty("password"));
driver.findElement(By.id("SignIn")).click();
System.out.println("URL ::" + prop.getProperty("URL"));
System.out.println("User name::" +prop.getProperty("username"));
System.out.println("Password::" +prop.getProperty("password"));
}
}
The below is the Output after executing the program: We are passing the properties values to the webdriver and printing the values at end
URL ::http://gmail.com
User name::testuser
Password::password123
We can also get all the key value pairs in the properties file using the below java program:
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.Properties;
public class ReadFileData {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File
("D:/Dev/ReadData/src/datafile.properties");
FileInputStream fileInput = null;
try {
fileInput = new FileInputStream(file);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Properties prop = new Properties();
try {
prop.load(fileInput);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Enumeration KeyValues = prop.keys();
while (KeyValues.hasMoreElements()) {
String key = (String) KeyValues.nextElement();
String value = prop.getProperty(key);
System.out.println(key + ":- " + value);
}
}
}
We have not used individual property name to get the KeyValue in the above program. It will get all the key values which are available in the .properties file
The Output of the above program:
URL:- http://gmail.com
password:- password123
username:- testuser
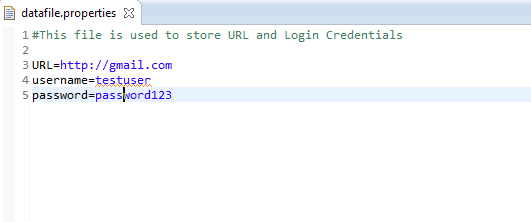
The below is the sample properties file that was used for the above tests. Remember white space between the property name and property value is always ignored. The following is the example.
username=testuser
username = testuser
How to create properties file?
Navigate to File menu -> New -> Click on File
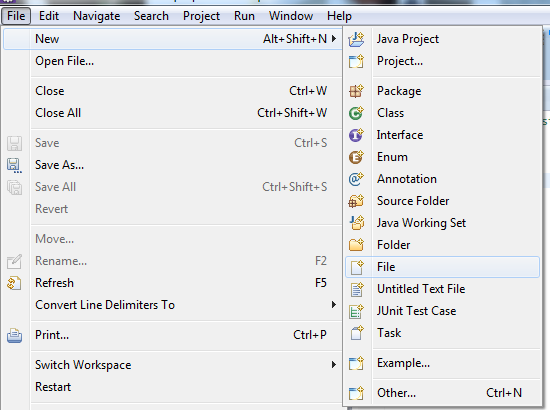
The only thing we need to do is, give the file name and give the extension as '.properties'. (Example: dataFile.properties)

____________________________________________
Read an Excel (.xlsx) file using Apache POI
As we know the main difference with Java JXL which does not support the Excel 2007 ".xlsx" file format. It only supports the old BIFF (binary) ".xls" format. Where as Apache POI supports both xls and xlsx file formats.
To read an Excel 2007 (.xlsx) we need to use XSSF (XML SpreadSheet Format) and we will use the below classes to work with xlsx files by importing the below statements
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFCell;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFRow;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFSheet;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
// Will get the workbook instance for XLS and takes excel file to read
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(XlsxFileToRead);
// We will pass the name / index of the sheet which starts from '0'.
XSSFSheet sheet = workbook.getSheet("Sheet1");
or
XSSFSheet sheet=wb.getSheetAt(0);
//We will iterate all the rows in the sheet
Iterator rows = sheet.rowIterator();
//We will be iterating all the cells of the current row
Iterator cells = row.cellIterator();
Cells can be numeric, formula-based, string-based (text) or Blank cell. To get the CellType CellType getCellTypeEnum(), where the CellType is the enum describing the type of the cell. You can use this to compare value CellType
if(cell.getCellTypeEnum() == CellType.STRING){
//write your code here
}
Now lets us take an same example which was used to read xls file and the read the xlsx file content.
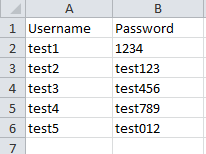
The above xlsx file has 2 columns 'Username' and 'Password' with 5 rows . We should be able to read the content using below example.
package com.read;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.Iterator;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFCell;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFRow;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFSheet;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
public class ReadXlsx {
public void readXLSXFile(String fileName) {
InputStream XlsxFileToRead = null;
XSSFWorkbook workbook = null;
try {
XlsxFileToRead = new FileInputStream(fileName);
//Getting the workbook instance for xlsx file
workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(XlsxFileToRead);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//getting the first sheet from the workbook using sheet name.
// We can also pass the index of the sheet which starts from '0'.
XSSFSheet sheet = workbook.getSheet("Sheet1");
XSSFRow row;
XSSFCell cell;
//Iterating all the rows in the sheet
Iterator rows = sheet.rowIterator();
while (rows.hasNext()) {
row = (XSSFRow) rows.next();
//Iterating all the cells of the current row
Iterator cells = row.cellIterator();
while (cells.hasNext()) {
cell = (XSSFCell) cells.next();
if (cell.getCellTypeEnum() == CellType.STRING) {
System.out.print(cell.getStringCellValue() + " ");
} else if (cell.getCellTypeEnum() == CellType.NUMERIC) {
System.out.print(cell.getNumericCellValue() + " ");
} else if (cell.getCellTypeEnum() == CellType.BOOLEAN) {
System.out.print(cell.getBooleanCellValue() + " ");
} else { // //Here if require, we can also add below methods to
// read the cell content
// XSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_BLANK
// XSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_FORMULA
// XSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_ERROR
}
}
System.out.println();
try {
XlsxFileToRead.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ReadXlsx readXlsx = new ReadXlsx();
readXlsx.readXLSXFile("C:/testXlsxRead.xlsx");
}
}
You may see below exception if you don't add 'xmlbeans-2.x.x'
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: org/apache/xmlbeans/XmlObject
And you may also come across the below exception if you don't add jar 'poi-ooxml-schemas-3.x-xxx'
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: org/openxmlformats/schemas/spreadsheetml/x2006/main/CTSheet
The below is the other exception that you get, if we don't add jar 'dom4j-1.x.x '
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: org/dom4j/DocumentException
If you are using Maven project, please add below two dependencies
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.poi/poi -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi</artifactId>
<version>3.17</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.poi/poi-ooxml -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi-ooxml</artifactId>
<version>3.17</version>
</dependency>
After adding all the jars the program will get executed successfully.
Output of the above program should look like below:
Username Password
test1 1234.0
test2 test123
test3 test456
test4 test789
test5 test012
_____________________________
Database testing using Java, Selenium, TestNG example
we will discuss how to perform database testing in different environments and pass the parameters to different methods in a simple way.
To do this, first we need to create a class to establish Database connection and take care of executing the database query in environment which we specify in Test. When ever we are expecting a list of values, we should make sure to save the ResultSet in a List. And when we are sure that ResultSet returns only a single value, we should save that in String.
In the below example we have given both the methods 'executeSQLQuery_List(String testEnv, String sqlQuery)' which returns list of values based on the query and 'executeSQLQuery(String testEnv, String sqlQuery)' returns only a string value.
Now let us first create a class and call it as 'DataBaseConnector.class'.
/**
* Created by VISISHTA on 12/19/2015.
*/
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class DataBaseConnector {
private static String dbusername;
private static String dbpassword;
//Should be defined as jdbc:mysql://host:port/database name
private static String databaseURLQA= "jdbc:mysql://qahost:22020/easy";
private static String databaseURLSTAGE= "jdbc:mysql://stagehost:2020/easyDB";
private static String databaseURLPRODUCTION= "jdbc:mysql://prodhost:2020/easyDB";
public static String executeSQLQuery(String testEnv, String sqlQuery) {
String connectionUrl="";
Connection connection;
String resultValue = "";
ResultSet rs;
//To connect with QA Database
if(testEnv.equalsIgnoreCase("QA")){
connectionUrl = databaseURLQA;
dbusername = "root";
dbpassword = "root";
}
//To connect with Stage Database
else if(testEnv.equalsIgnoreCase("STAGE")) {
connectionUrl = databaseURLSTAGE;
dbusername = "root";
dbpassword = "stagepassword";
}
//To connect with Production Database
else if(testEnv.equalsIgnoreCase("PRODUCTION")) {
connectionUrl = databaseURLPRODUCTION;
dbusername = "root";
dbpassword = "prodpassword";
}
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
}catch(ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(connectionUrl,dbusername,dbpassword);
if(connection!=null) {
System.out.println("Connected to the database...");
}else {
System.out.println("Database connection failed to "+testEnv+" Environment");
}
Statement stmt = connection.createStatement();
rs=stmt.executeQuery(sqlQuery);
try {
while(rs.next()){
resultValue = rs.getString(1).toString();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
catch (NullPointerException err) {
System.out.println("No Records obtained for this specific query");
err.printStackTrace();
}
connection.close();
}catch(SQLException sqlEx) {
System.out.println( "SQL Exception:" +sqlEx.getStackTrace());
}
return resultValue;
}
public static ArrayList<String> executeSQLQuery_List(String testEnv, String sqlQuery) {
String connectionUrl="";
Connection connection;
ArrayList<String> resultValue = new ArrayList<String>();
ResultSet resultSet;
//To connect with QA Database
if(testEnv.equalsIgnoreCase("QA")){
connectionUrl = databaseURLQA;
dbusername = "root";
dbpassword = "root";
}
//To connect with Stage Database
else if(testEnv.equalsIgnoreCase("STAGE")) {
connectionUrl = databaseURLSTAGE;
dbusername = "root";
dbpassword = "stagepassword";
}
//To connect with Production Database
else if(testEnv.equalsIgnoreCase("PRODUCTION")) {
connectionUrl = databaseURLPRODUCTION;
dbusername = "root";
dbpassword = "prodpassword";
}
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
}catch(ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(connectionUrl,dbusername,dbpassword);
if(connection!=null) {
System.out.println("Connected to the database");
}else {
System.out.println("Failed to connect to "+testEnv+" database");
}
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
resultSet=statement.executeQuery(sqlQuery);
try {
while(resultSet.next()){
int columnCount = resultSet.getMetaData().getColumnCount();
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
for(int iCounter=1;iCounter<=columnCount; iCounter++){
stringBuilder.append(resultSet.getString(iCounter).trim()+" ");
}
String reqValue = stringBuilder.substring(0, stringBuilder.length()-1);
resultValue.add(reqValue);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
catch (NullPointerException ex) {
System.out.println("No Records found for this specific query" +ex.getStackTrace());
}
finally {
if (connection != null) {
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException ex) {
System.out.println( "SQL Exception:" +ex.getStackTrace());
}
}
}
}catch(SQLException sqlEx) {
System.out.println( "SQL Exception:" +sqlEx.getStackTrace());
}
return resultValue;
}
}
In the above example, we have hard coded values of database URL and credentials, But you can store them in a properties file and get these values. You can check here for more details on 'Read data from Properties file using Java Selenium'
Below is the database which is used for this example :

Now we will create 'SeleniumDataBaseTestingExample.class' which will have two tests to make use of both the methods defined in 'DataBaseConnector.class'
/**
* Created by VISISHTA on 12/17/2015.
*/
import org.testng.Assert;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class SeleniumDataBaseTestingExample {
//Test to verify Employee ID '1' has employee name 'Jack'
@Test(priority = 1)
public void testVerifySpecificRecord() {
String sqlQuery = "select EmpName from employee WHERE EmpId="1"";
String expectedEmpName = "Jack";
//Getting employee name by Id
String actualEmpNameById = DataBaseConnector.executeSQLQuery("QA", sqlQuery);
System.out.println("Employee name retrieved from database :" + actualEmpNameById);
Assert.assertEquals(expectedEmpName, actualEmpNameById);
}
//Test to verify Employee table has a record with employee name 'Jack'
@Test(priority = 2)
public void tesVerifyListOfRecords() {
boolean flag = false;
List<String> listOfDBValues = new ArrayList<String>();
String expEmployeeName = "Jack";
String sqlQuery = "select EmpName from employee";
//Getting list of employee names from employee table
listOfDBValues = DataBaseConnector.executeSQLQuery_List("QA", sqlQuery);
for (String strName : listOfDBValues) {
if (strName.equalsIgnoreCase(expEmployeeName)) {
flag = true;
break;
}
}
Assert.assertTrue(flag, "Retrieved values are not matching with Expected values");
}
}
In the above example, 'testVerifySpecificRecord' test is calling 'executeSQLQuery' method and expecting a String to validate. And second test 'tesVerifyListOfRecords' is expecting list of employee names and then compare with the expected employee name in the list.
_________________________________-----
Comments
Post a Comment