Java Basics:Return type in Java
Return type in Java | Example Program
Java Return Statement
Return type in Java | We know that a method is a function declared inside a class that contains a group of statements.
It is used to perform certain tasks or processing of data in the program to yield the expected results.
A method can accept data from outside and can also return the results. To return the result, a return statement is used inside a method to come out of it to the calling method.
In Java, return is a keyword that is used to exit from the method only with or without returning a value. Every method is declared with a return type in java and it is mandatory for Java methods.
Return type may be a primitive data type like int, float, double, a reference type, or void type which represents “return nothing”. i.e, they don’t give anything back.
When a method is called, the method may return a value to the caller method.
Let’s take an example program to understand the concept of java return type better.
Here, we will write a program to return the square of a number from a method. Look at the following source code.
Program source code 1:
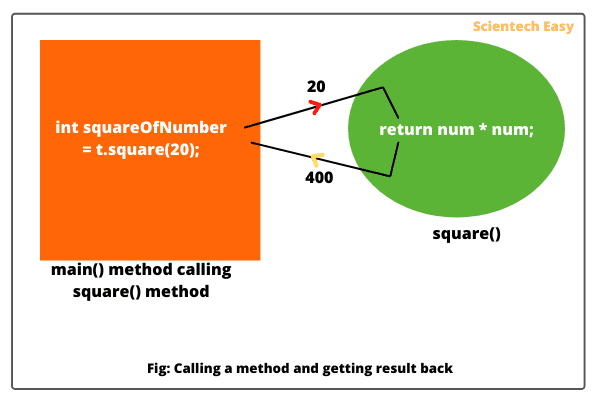
Explanation: Look at the below figure and understand the explanation that will help you to understand better.
a. In this example program, we have created a method named square(). This method accepts an integer value and calculates the square of it.
After calculating square of value, square() method returns that value to the main() method that is the calling method.
b. Inside the main() method, we are calling square() method using object reference variable t and passing 20 to it as follows: t.square(20);.
c. To get the result returned from the square() method, we have taken a variable “squareOfNumber” of type int as follows: int squareOfNumber = t.square(20);.
d. int before a method name specifies the type of value returned by the method.
e. After method name, we wrote int num as a parameter that receives an integer value into the method. We are passing a value 20 to the method at the time of calling from main method.
f. Now to calculate the square value and return it, we have used return statement (return num * num;) inside the square() method.
Thus, a return statement in java is used to return a value from a method. It can return only one value at a time. When a return statement is used inside the method, the flow of execution comes out of it and goes back to the caller method.
Types of Methods Declaration based on Return type in Java
1. Method with void type:
For example:
Here, the void represents “return nothing”. A return type void is used when there is no return value.
2. Methods with return type and value:
If a method is having int, double, float, etc other than void, we must return a value compatible with the declared return type by using the return statement.
If you are not returning any value, it will generate an error message like ” missing return statements “. Let’s take some examples related to it.
Code 2 is an invalid code because, inside the method, the return statement must be the last statement of method.
How to return primitive values like int, float, double?
Let’s take an example program where we will return primitive values like int, float, and char to methods m1(), m2(), and m3() respectively.
Program source code 2:
In this example program, methods m1(), m2(), and m3() are returning primitive value to the main method that is calling method.
But at the project level, generally, we do not return primitive value. At the real-time project level, we return an object as returning value.
How to return class object in Java?
In the realtime project, we return different class objects as returning values. You must remember that Java cares about type. In other words, you cannot return a Student when the return type is declared as an Employee.
For example:
Here, m1() method’s return type is Employee.
Let’s take an example program based on this concept.
Consider a project in which there are three modules like Student, Employee, and School in an application. We will create a class for each module.
We will declare m1() and m2() methods with return type Student and Employee class respectively in the school class. See the coding given below.
Program source code 3:
How to return current or same class object in Java?
In the last example program, we have returned different class objects but we can also return the current class object at the project level. Let’s understand this concept with the help of an example.
Ways to return current/same class object
There are two ways to return the current or same class object.
1. If the method’s return type is a current class, you create an object of the class and return object reference variable.
2. You can also return a value direct using “this” keyword which represents the current class object. But at the project level, it is always recommended to use the second approach.
Let’s take an example program where we will use both approaches to return the same class object.
Program source code 4:
How to return a variable in Java programming?
Let us consider an example to return a variable.
Here, we have declared an m1() method with return type int and parameter a. Since m1() method’s return type is an integer. So, we must return an int value. Therefore, we will return ‘a’ as a value of int type.
Generally, there are three cases for returning a variable in Java.
Case 1:
The above code contains both instance and local variables. In this case, the first priority will always go to the local variable and will return ‘a’ as a value.
Case 2:
In this case, it will return the instance value due to no local variable.
Case 3:
It will return instance variable due to using ‘this’ keyword. So, remember these three very important cases for the project level.
Let’s implement these three cases in the programs one by one.
Program source code 5:
Program source code 6:
Program source code 7:
3. Method with return type and without value:
For example:
A method is able to return a value but holding the value is optional. So, it is always recommended to hold the return value.
Let’s create a program where we will declare a method with return type but without value.
Program source code 8:
Can we declare return statement inside main method in Java?
If we write return statement inside the main method, the entire program or application will be terminated and the next statement after return statement will not be executed in the program.
Let’s take a program and see what happens?
Program source code 9:
In this example program, we can also write System.exit(0); at the place of return statement to terminate the program. Here, exit(0) is a static method defined by class System. Therefore, it can be called by using class name.
Comments
Post a Comment